A bottleneck in your PC can significantly limit its performance, holding back the potential of even the most powerful hardware. Whether you’re gaming, editing, or running intensive workloads, understanding and addressing bottlenecks ensures your system performs at its best. This guide will help you identify, fix, and prevent bottlenecks so you can maximize your hardware’s efficiency.
What is a PC Bottleneck?
A bottleneck occurs when one component in your PC limits the performance of the others. Think of it like traffic on a two-lane road that suddenly narrows to one lane: even if the cars (data) are moving quickly before the narrowing, they will slow down considerably at the bottleneck.
In a PC, bottlenecks happen when one component, like the CPU or GPU, can’t keep up with the workload, causing delays in performance.
Why Bottlenecks Matter
- Wastes the performance of other components.
- Reduces frame rates and smoothness in games.
- Delays workflows like video editing and rendering.
- Results in poor value for money spent on overpowered components.
Common Myths About Bottlenecks
- “Only old PCs get bottlenecks.”
Even new systems can suffer bottlenecks if components are mismatched or improperly configured. - “Bottlenecks are always bad.”
Some level of bottlenecking is normal. Perfect balance is rarely achievable. - “A better GPU will fix everything.”
Upgrading your GPU alone won’t help if your CPU or RAM is the real issue. - “Higher FPS means no bottlenecks.”
A system might still have bottlenecks, even if it delivers high FPS.
How to Identify a Bottleneck
Before fixing bottlenecks, you need to identify where they are. Here’s how:
Step 1: Monitor CPU and GPU Usage (Utilization)
Monitoring CPU and GPU usage allows you to see which component is working hardest and therefore potentially limiting the performance of the others. To do this:
- Open Task Manager (Ctrl + Shift + Esc) or use MSI Afterburner.
- Monitor CPU and GPU utilization while running a demanding game or application.
- If the CPU usage is consistently near 100% while GPU usage is significantly lower, the CPU is bottlenecking the system.
- If the GPU usage is consistently near 100% while CPU usage remains low, the GPU is the bottleneck.
Regular monitoring helps in identifying bottlenecks before they impact performance significantly. To learn more about monitoring PC performance, refer to our article on How to Monitor Your PC’s Performance for Bottlenecks.
Step 2: Benchmark Your System
Use benchmarking tools like 3DMark (for graphics performance) or Cinebench (for CPU performance) to analyze your PC’s performance. Benchmarks measure component capabilities and help identify weak links.
Compare results to similar systems online to spot inconsistencies and see if your components are performing as expected. While tools like UserBenchmark or PassMark can provide general comparisons, be aware that their scoring methodologies can be controversial, so consider them as just one piece of the puzzle.
Step 3: Identify Signs of Bottlenecks
- Low frame rates in games despite having a high-end GPU.
- CPU or GPU maxed out while other components remain underutilized.
- Long load times caused by slow storage.
- Slow system responsiveness during multitasking.
Types of PC Bottlenecks and How to Fix Them
Let’s explore the most common types of PC bottlenecks and strategies for resolving them.
1. CPU Bottleneck
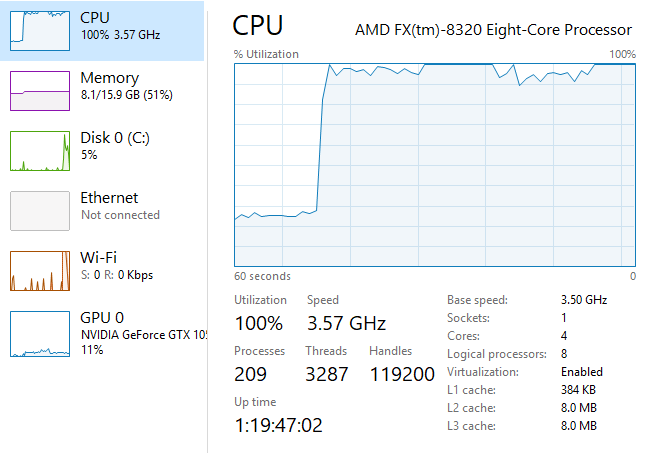
Why it happens: The CPU cannot keep up with the GPU’s demands, especially in CPU-heavy games or workloads.
Signs:
- CPU usage at 90-100%.
- GPU usage remains significantly lower (~60-70%).
- Stuttering or low FPS in CPU-intensive games.
How to Fix CPU Bottlenecks:
- Lower CPU-Intensive Settings: Reduce draw distance, crowd density, and physics calculations.
- Overclock the CPU: Use tools like Intel XTU or Ryzen Master to boost CPU clock speeds (with caution).
- Close Background Processes: Use Task Manager to close unnecessary apps consuming CPU resources.
- Upgrade to a Better CPU: Match the CPU to your GPU (e.g., pair an RTX 4080 with at least an i7 or Ryzen 7).
CPU bottlenecks are common, especially in gaming setups with high-performance GPUs. Dive deeper into CPU-related bottlenecks in our article on Understanding CPU Agent Bottlenecks and Their Effect on FPS.
2. GPU Bottleneck
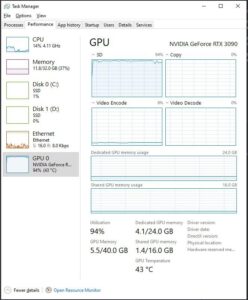
Why it happens: The GPU cannot render frames fast enough to match CPU performance.
Signs:
- GPU usage at 90-100%.
- CPU usage remains low (~40-50%).
- Low frame rates in GPU-intensive games.
How to Fix GPU Bottlenecks:
- Lower Graphical Settings: Reduce texture quality, shadows, anti-aliasing, and resolution.
- Enable DLSS or FSR: Use NVIDIA DLSS or AMD FSR to improve performance in supported games.
- Overclock the GPU: Use tools like MSI Afterburner to increase GPU clock speeds (carefully).
- Upgrade to a Better GPU.
3. RAM Bottleneck
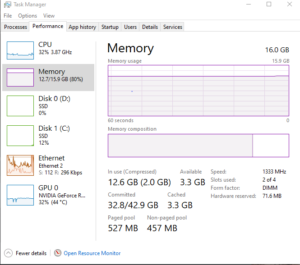
Why it happens: Insufficient or slow RAM limits system performance.
Signs:
- Stuttering or freezes during gameplay.
- Applications crash or run slowly.
- Slow system responsiveness during multitasking.
How to Fix RAM Bottlenecks:
- Add More RAM: Upgrade to at least 16GB.
- Increase RAM Speed: Enable XMP (Extreme Memory Profile) in BIOS to ensure RAM runs at its advertised speed.
Insufficient RAM can be a major bottleneck in systems designed for multitasking or gaming. Explore how much RAM your system needs in our guide on RAM Bottlenecks: How Much RAM Do You Really Need?.
Tools to Identify and Fix Bottlenecks
- MSI Afterburner: Monitors CPU/GPU usage, temperatures, and FPS.
- 3DMark & Cinebench: Benchmarking tools to compare system performance.
- HWMonitor: Tracks component temperatures, voltages, and fan speeds, helpful for identifying thermal throttling.
- CapFrameX: Analyzes frame-time data to pinpoint stuttering and inconsistencies in frame delivery.
Conclusion
By identifying and addressing bottlenecks, you can maximize your PC’s performance and avoid wasting money on mismatched components. Use monitoring tools, analyze performance, and make targeted upgrades to enjoy smoother gameplay and faster workflows. Avoiding bottlenecks requires careful planning and a balanced selection of components. To ensure compatibility and a seamless build, refer to our guide on Build a Seamless PC: A Guide to Component Compatibility.