Introduction
Is your computer underperforming? You might have a bottleneck. A bottleneck occurs when one component in a system limits the potential of other components, like a narrow point in a pipe restricting water flow; the overall flow is limited by the narrowest section. Understanding hardware bottlenecks is crucial for optimizing performance across various tasks. Whether you’re a gamer, a laptop user, or a content creator, identifying bottlenecks can help you make informed decisions about upgrades or configurations tailored to your specific needs. This guide explores tailored bottleneck calculators for specific user groups and provides practical advice for maximizing performance. Remember, the “best” configuration depends entirely on your intended use.
A visual representation of a hardware bottleneck: The narrow section in the pipeline symbolizes the limiting component (e.g., CPU, GPU, or RAM), restricting the overall system performance and efficiency.
Understanding the Bottleneck Concept in More Detail
A bottleneck isn’t always a simple “one component is 100% utilized while others are idle” scenario. It can be more nuanced:
CPU Bottleneck
The CPU can’t feed data to the GPU fast enough, resulting in the GPU waiting for instructions and underutilizing its potential. This is more common at lower resolutions (like 1080p) where the CPU has to process more frames.
GPU Bottleneck
The GPU is working at its full capacity, while the CPU has spare processing power. This is more common at higher resolutions (like 4K) where the GPU has to render more pixels.
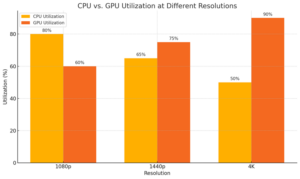
Here is the side-by-side bar chart comparing CPU and GPU utilization at different resolutions (1080p, 1440p, 4K). The chart highlights how utilization shifts between the CPU and GPU as resolution increases. Let me know if you’d like any adjustments!
Other Bottlenecks
Bottlenecks can also occur with:
- RAM: Insufficient capacity or slow speed.
- Storage: Slow hard drives causing long loading times.
- Motherboard Chipset: Limited bandwidth.
A flow diagram highlighting CPU, GPU, RAM, and storage as potential bottleneck sources, with brief descriptions of each.
Bottleneck Calculators for Gaming
Gaming systems require a balance between the CPU and GPU to ensure smooth gameplay. A mismatch between these components can lead to frame drops, stuttering, or underutilized hardware. For example, pairing an Intel i9-13900K with an RTX 4090 at 1080p could create a CPU bottleneck in some titles, while at 4K, the GPU would likely be the limiting factor.
Recommended Calculators and Specific Considerations
- PC-Build’s Bottleneck Calculator: This tool evaluates the compatibility between your CPU and GPU, providing detailed insights into performance discrepancies. Note: These calculators provide estimates and should be considered alongside real-world benchmarks.
- UserBenchmark: While not exclusively a bottleneck calculator, it offers comparative performance analysis for various components. Caution: UserBenchmark’s methodology has been criticized for favoring certain hardware manufacturers.
- Game-Debate’s Hardware Tool: Ideal for predicting game-specific performance based on your setup.
It’s crucial to assess the accuracy of these tools to ensure they provide reliable insights. Learn more about the accuracy of these tools in our article on How Accurate Are Bottleneck Calculators?.
Considerations
- Resolution and Frame Rate Goals: Higher resolutions like 1440p or 4K shift the workload to the GPU, reducing CPU bottlenecks. Higher refresh rate monitors also put more demand on the CPU.
- Overclocking Potential: Overclocking the CPU or GPU can alleviate bottlenecks but may require better cooling and careful monitoring for stability.
- Game Optimization: Some games are CPU-intensive (e.g., strategy games, simulations), while others rely heavily on the GPU (e.g., first-person shooters, graphically demanding open-world games).
- Diagnostics: Running diagnostic tools like MemTest86 for RAM or CrystalDiskInfo for storage health can identify potential software conflicts or failing hardware beyond bottlenecks.
Remember: Bottleneck calculators are a valuable starting point, but real-world testing with benchmarks and user reviews for specific games can provide a more comprehensive picture of performance.
Bottleneck Calculators for Laptops
Laptops present unique challenges due to their compact design and thermal constraints. Bottleneck analysis for laptops often focuses on thermal throttling and component compatibility. Laptops with integrated graphics often struggle with graphically intensive games, leading to significant performance bottlenecks.
Recommended Tools and Thermal Considerations
- HWInfo: Provides real-time data on component usage and thermal performance.
- ThrottleStop: A powerful tool for monitoring and reducing CPU throttling.
- Notebookcheck’s Performance Charts: A comprehensive resource for evaluating laptop hardware performance.
Considerations
- Thermal Management: Ensure proper cooling with external fans or cooling pads to mitigate throttling.
- Integrated vs. Dedicated GPUs: Integrated GPUs often share resources with the CPU, potentially creating bottlenecks in gaming or graphical workloads.
- Power Profiles: Adjusting performance settings can balance power consumption and performance.
- Background Processes: Laptops often run more background processes than desktops, impacting CPU performance. Close unnecessary applications to free up resources.
- Driver Updates: Outdated drivers can cause performance issues and create perceived bottlenecks. Ensure all drivers, especially graphics drivers, are up to date.
Bottleneck Calculators for Content Creation
Content creation tasks like video editing, 3D rendering, and graphic design require a harmonious balance of CPU, GPU, and RAM. Misaligned components can slow down workflows and reduce productivity. Using a slow HDD for video editing can create a severe bottleneck, even with a powerful CPU and GPU.
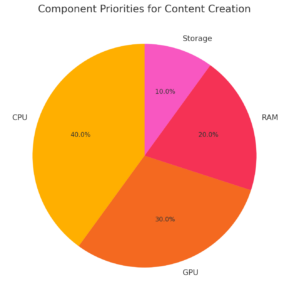
Relative importance of hardware components for content creation: The CPU plays the most significant role, followed by the GPU, while RAM and storage contribute to overall efficiency depending on the task
Recommended Tools and Specific Software Considerations
- Puget Systems’ Benchmark Tools: Tailored for professional applications like Adobe Premiere Pro, After Effects, and DaVinci Resolve.
- Blender’s Benchmark Tool: (Built into Blender, access it through Edit > Preferences > System > Benchmark)
- PassMark’s Performance Test: Offers detailed insights into CPU, GPU, and RAM performance.
Considerations
- Software Optimization: Some applications, like Photoshop, benefit more from CPU performance, while others, like Blender, leverage the GPU. Multi-core CPUs are generally beneficial for tasks like video encoding and rendering, while higher clock speeds can improve performance in tasks like 3D modeling and single-threaded applications.
- RAM Capacity: Content creation often requires high RAM capacity (16GB or more) for smooth performance.
- RAM Speed: Faster RAM (higher MHz) can improve performance in memory-intensive tasks like video editing.
- Storage Type and Speed: NVMe SSDs offer significantly faster read and write speeds than SATA SSDs, drastically reducing loading times and improving responsiveness in workflows.
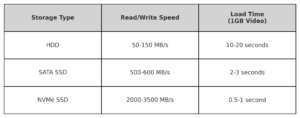
Compact comparison of storage types: HDDs offer the slowest speeds and longest load times, while SATA SSDs and NVMe SSDs significantly enhance performance with faster read/write speeds and reduced loading times.
Summary of Recommended Tools
| Use Case | Recommended Tools | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Gaming | PC-Build’s Bottleneck Calculator, UserBenchmark, Game-Debate’s Hardware Tool | Resolution, Frame Rate, Overclocking, Game Optimization, Diagnostics |
| Laptops | HWInfo, ThrottleStop, Notebookcheck’s Performance Charts | Thermal Management, Integrated vs. Dedicated GPUs, Power Profiles, Background Processes, Driver Updates |
| Content Creation | Puget Systems’ Benchmark Tools, Blender’s Benchmark Tool (Built-in), PassMark’s Performance Test | Software Optimization (Multi-core vs. Clock Speed), RAM Capacity, RAM Speed, Storage Speeds |
Understanding and utilizing bottleneck calculators can aid in optimizing your system’s performance. For a broader understanding of PC bottlenecks, refer to our Ultimate Guide to PC Bottlenecks and How to Avoid Them.
Conclusion
Bottleneck calculators are invaluable tools for optimizing system performance across various use cases. Gamers should focus on balancing CPU and GPU power, laptop users must address thermal constraints and consider futureproofing, and content creators need to ensure compatibility with software demands, considering both multi-core performance and clock speeds. By using the recommended calculators, running diagnostics, and following tailored advice, you can enhance performance and make cost-effective upgrades.
Ready to optimize your system? Use the recommended tools, research your specific needs, and don’t hesitate to join online communities dedicated to PC building or content creation for further guidance!