In today’s fast-paced digital world, the amount of Random Access Memory (RAM) in your device plays a critical role in determining its overall performance. Whether you’re a casual user, a hardcore gamer, or a professional content creator, understanding how much RAM you need can make a significant difference. This guide will help you assess your RAM requirements based on your use case and optimize your device’s performance.
How RAM Affects Performance
RAM serves as a temporary storage space for data that your computer is currently processing. When you run applications or process data, your system stores this information in RAM. Insufficient RAM can lead to bottlenecks, where the system resorts to using slower storage solutions, like your hard drive or SSD, to compensate. This process is called swapping or paging, where data is moved between RAM and storage. Because storage is significantly slower than RAM, this can result in significantly longer loading times for applications (e.g., several seconds instead of a fraction of a second), noticeable delays when switching between programs, system freezes, and in severe cases, “thrashing,” where the system spends almost all its time swapping data, making it nearly unusable.
On the other hand, having excess RAM ensures smooth multitasking, faster data access, and reduced system slowdowns. However, there’s a point of diminishing returns where adding more RAM yields little to no noticeable improvement. Knowing how much RAM you truly need is key to making an informed decision.
Selecting the appropriate RAM ensures your system runs efficiently without bottlenecks. Learn more about component compatibility in our guide on Building a Seamless PC.
RAM Requirements for Different Use Cases
For Gaming
Gaming often demands significant RAM, especially for modern AAA titles. Here’s what you need to consider:
- Minimum Recommendation: 8 GB – Suitable for older or less demanding games.
- Standard for Most Games: 16 GB – Allows smooth gameplay with modern AAA titles like Cyberpunk 2077, Red Dead Redemption 2, or Assassin’s Creed Valhalla, and provides room for background tasks like Discord or web browsers. Less demanding or older games may run adequately on 8GB.
- High-End Gaming: 32 GB – Ideal for gamers who stream, use mods, or play resource-intensive games at high resolutions.
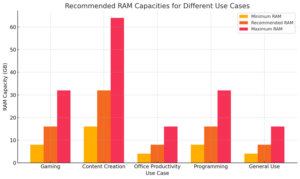
Recommended RAM Capacities for Different Use Cases: This bar chart illustrates the minimum, recommended, and maximum RAM requirements for activities like gaming, content creation, office productivity, programming, and general use. It helps users quickly identify the suitable RAM capacity for their specific needs.
For Content Creation
Content creation tasks such as video editing, graphic design, and 3D rendering demand significant memory resources.
- Basic Editing and Design: 8-16 GB – Sufficient for hobbyists or lightweight applications.
- Professional Use: 32 GB – Optimal for 4K video editing in Adobe Premiere Pro, complex Photoshop projects with multiple layers and filters, or CAD applications like AutoCAD.
- Advanced Workflows: 64 GB or more – Recommended for large-scale 3D rendering or multi-tasking across demanding software.
For Office Work and Productivity
Typical productivity tasks like using spreadsheets, word processors, and web browsers are less demanding.
- Basic Use: 4-8 GB – Adequate for simple tasks like email, browsing, and document editing.
- Heavy Multitasking: 16 GB – Ideal for users who frequently switch between multiple tabs and apps.
For Programming
Developers and programmers have varying RAM needs depending on their projects.
- Basic Coding: 8 GB – Suitable for lightweight programming languages and small projects.
- Advanced Development: 16-32 GB – Necessary for working with virtual machines (each VM essentially runs a separate operating system, requiring its own dedicated memory), large IDEs, or data-intensive tasks.
For General Users
If you primarily use your device for streaming, browsing, and occasional gaming:
- Casual Use: 4-8 GB – Handles basic everyday tasks.
- Enhanced Performance: 16 GB – Ensures smooth operation, even with multiple browser tabs and apps open.
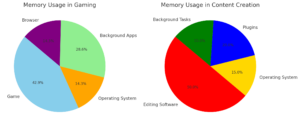
Memory Usage Distribution for Gaming and Content Creation: These pie charts depict typical RAM allocation in two scenarios. For gaming, the majority is used by the game itself, followed by background apps, the OS, and the browser. For content creation, editing software dominates, complemented by plugins, the OS, and background tasks, highlighting the intensive memory needs of such activities.
RAM Capacity and Multitasking Capability
A tabular representation of how various RAM capacities handle multitasking:
| RAM Size | Number of Open Applications | Performance Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 4 GB | 4-5 apps | Noticeable slowdowns |
| 8 GB | 8-10 apps | Adequate for light use |
| 16 GB | 12-20 apps | Smooth performance |
| 32 GB | 20+ apps | Excellent performance |
Understanding RAM Speed and Timings
When buying RAM, capacity isn’t the only factor to consider. Speed and timings also impact performance.
- RAM Speed: Measured in MHz, higher speeds can improve data transfer rates. However, real-world performance gains depend on your CPU and motherboard compatibility. This means that your CPU and motherboard must support the RAM’s speed for it to run at its advertised frequency. If they don’t, the RAM will run at a lower speed. While higher speed RAM can be beneficial for gaming and content creation, the difference in real-world performance may be less noticeable for general office work.
- CAS Latency (CL): This indicates the delay, measured in clock cycles, before the RAM responds to a request. Lower latency is better, but the difference is often negligible for general use.
- Multi-Channel Configuration: Using multiple RAM modules (dual-channel, quad-channel, etc.) allows the memory controller to access data from multiple modules simultaneously, increasing memory bandwidth and improving performance.
- XMP/DOCP Profiles: XMP (Intel Extreme Memory Profile) and DOCP (AMD’s equivalent) are pre-defined profiles stored on the RAM modules that allow you to easily set the RAM to its advertised speed and timings in your computer’s BIOS, ensuring both optimal performance and stability. This ensures optimal performance without manual configuration.
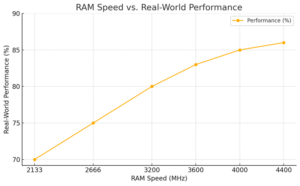
RAM Speed vs. Real-World Performance: This line chart demonstrates the diminishing returns on real-world performance as RAM speed increases. While higher speeds offer marginal gains, the improvement plateaus, emphasizing the importance of balancing speed with other system components.
Understanding RAM requirements is just one aspect of preventing system bottlenecks. For a comprehensive overview of PC bottlenecks, refer to our Ultimate Guide to PC Bottlenecks and How to Avoid Them.
Conclusion
Your RAM needs depend heavily on your specific use case; while 8 GB may suffice for casual users, 16 GB or more is often beneficial for gamers and professionals, and considering RAM speed, timings, and configuration (especially multi-channel setups) can further optimize performance. When purchasing RAM, assess your current and future needs to avoid over- or under-spending. A well-balanced choice ensures a smoother, more efficient computing experience.